How to dose CEPROTIN
CEPROTIN dosing schedule for acute episodes/short-term prophylaxis
and long-term prophylaxis1
Initiate treatment with CEPROTIN under the supervision of a physician experienced in replacement therapy with coagulation factors/inhibitors where monitoring of protein C activity is feasible.1
The dose, administration frequency and duration of treatment with CEPROTIN depends on the severity of the protein C deficiency, the patient’s age, the clinical condition of the patient and the patient’s plasma level of protein C. Therefore, adjust the dose regimen according to the pharmacokinetic profile for each individual patient.1
CEPROTIN DOSING SCHEDULE FOR ACUTE EPISODES, SHORT-TERM PROPHYLAXYS AND LONG-TERM PROPHYLAXIS1,a
|
INITIAL DOSEb |
SUBSEQUENT 3 DOSESb |
MAINTENANCE DOSEb |
|
| acute episode / short-term prophylaxisc |
100 - 200 IU/kg |
60 - 80 IU/kg Q 6 hours |
45 - 60 IU/kg Q 6 OR 12 hours |
|
long-term prophylaxis |
NA | NA |
45 - 60 IU/kg Q 12 hours |
bAdjust the dose according to the pharmacokinetic profile for each individual.
cContinue CEPROTIN until desired anticoagulation is achieved.
NA = Not applicable; Q = every
The measurement of protein C activity using a chromogenic assay is recommended for the determination of the patient’s plasma level of protein C before and during treatment with CEPROTIN. The half-life of CEPROTIN may be shortened in certain clinical conditions such as acute thrombosis, purpura fulminans and skin necrosis.1
In the case of an acute thrombotic event, it is recommended that protein C activity measurements be performed immediately before the next injection until the patient is stabilized. After the patient is stabilized, continue monitoring the protein C levels to maintain the trough protein C level above 25%.1
Patients treated during the acute phase of their disease may display much lower increases in protein C activity.
Coagulation parameters should also be checked. However, in clinical trials, data were insufficient to establish correlation between protein C activity levels and coagulation parameters.1
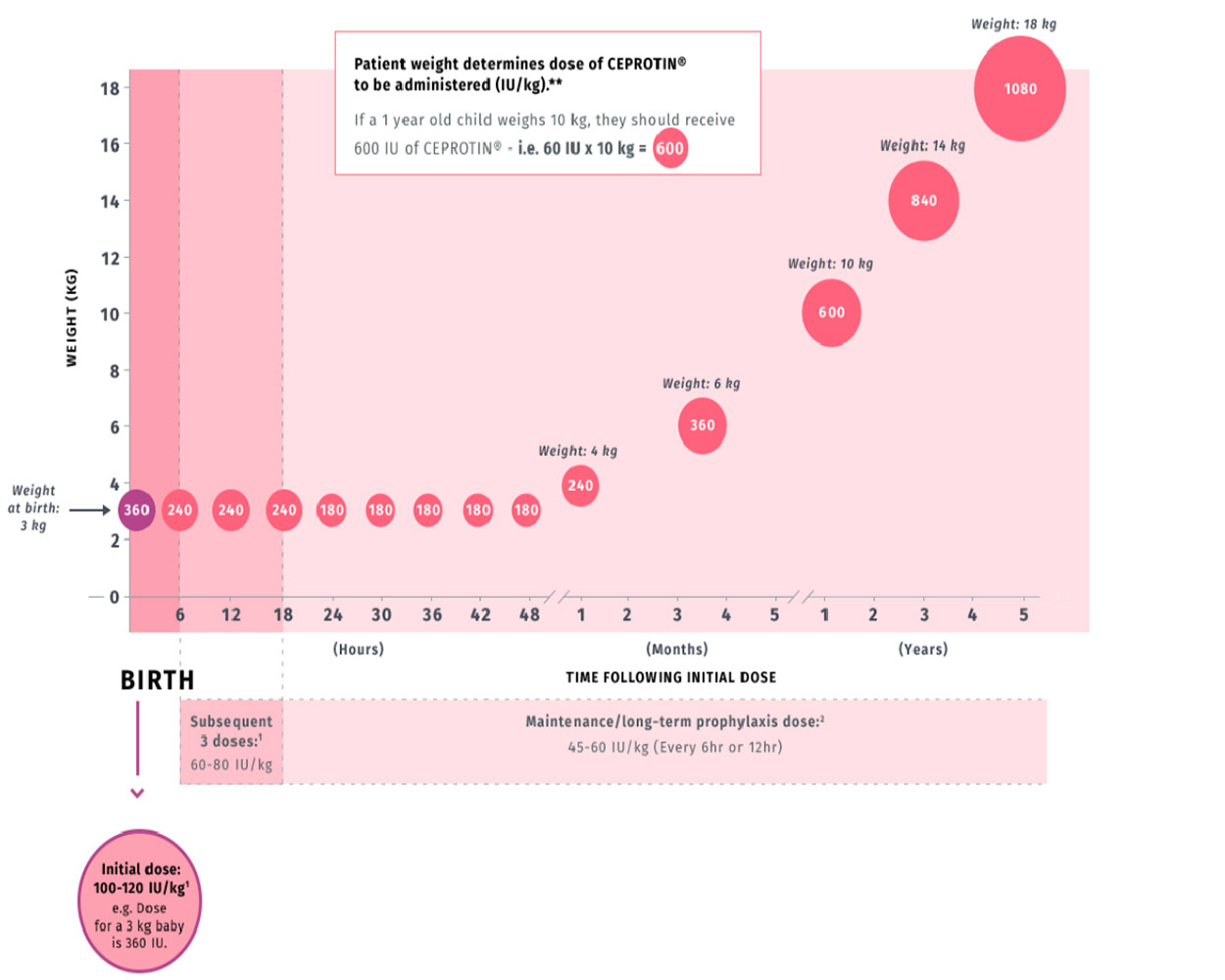
CEPROTIN dose calculation is based on patient weight
1
This graph is an example based on possible new patients born weighing 3 kg.
Consult the CEPROTIN Prescribing information before administering to any patient.
*Doses given are examples calculated using the maximum dose from the recommended range and estimated patient weight.
All doses listed in the below table are given in IUs.
Initiation of vitamin K antagonists
– In patients starting treatment with oral anticoagulants belonging to the class of vitamin K antagonists, a transient hypercoagulable state may arise before the desired anticoagulant effect becomes apparent. This transient effect may be explained by the fact that protein C, itself a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein, has a shorter half-life than most of the vitamin K-dependent proteins (i.e Factor II, IX and X).1
– In the initial phase of treatment, the activity of protein C is more rapidly suppressed than that of the procoagulant factors. For this reason, if the patient is switched to oral anticoagulants, protein C replacement must be continued until stable anticoagulation is obtained. Although warfarin-induced skin necrosis can occur in any patient. During the initiation of treatment with oral anticoagulant therapy, individuals with severe congenital protein C deficiency are particularly at risk.1
– During the initiation of oral anticoagulant therapy, it is advisable to start with a low dose of the anticoagulant and adjust this incrementally, rather than use a standard loading dose of the anticoagulant.1
AN INCREASE IN PLASMA PROTEIN C LEVELS WAS OBSERVED DURING THE DOSING TRIAL2
- The measurement of protein C activity using a chromogenic assay is recommended for the determination of the patient’s plasma level of protein C before and during treatment with CEPROTIN1
- The half-life of CEPROTIN may be shortened in certain clinical conditions such as acute thrombosis, purpura fulminans and skin necrosis1
- The dose, administration frequency and duration of treatment with CEPROTIN depends on the severity of the protein C deficiency, the patient’s age, the clinical condition of the patient and the patient’s plasma level of protein C1
- Adjust the dose regimen according to the pharmacokinetic profile for each individual patient1
- Patients treated during the acute phase of the disease may display a much lower increase in Protein C activity1
- Coagulation parameters should be checked1
- In clinical trials, data were insufficient to establish correlation between protein C activity levels and coagulation parameters
Pre- and Post- Infusion Protein C Activity Levels
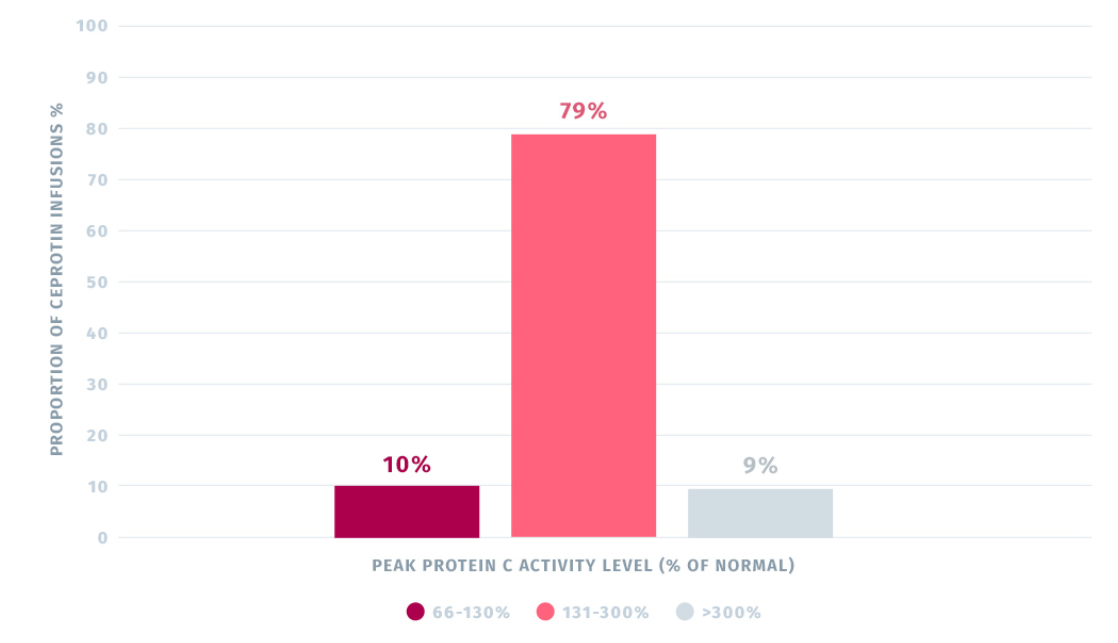
- Administration of CEPROTIN normalized plasma protein C activity levels in the trial.2
-
Results from the multi-center, open-label, non-randomized trial in patients with severe congenital protein C deficiency :
The median pre-first infusion PC activity level was 2.00 IU/dl and the median post-first infusion PC level was 165.0 IU/dl, based on an average infusion dose of 120 IU/kg body weight. Subsequent to first infusion, PC activity levels increased considerably from pre- to post-treatment.2
A total of 89% of post-infusion (peak) PC levels were within 66-300% (10% within 66-130% and 79% within 131-300% of normal), whereas 9% of the levels were >300% of normal.2
*Protein C activity was measured using the amidolytic test system. Protein C amidolytic activity is determined in comparison with a reference preparation calibrated against the 1st International Standard for Protein C in Plasma, code 86/622 (https://www.who.int/bloodproducts/catalogue/Fibr2015.pdf?ua=1).
Please refer to the full prescribing information for complete information on Dosage and Administration.1
Warnings and Precautions
Hypersensivity: CEPROTIN may contain trace amounts of mouse protein and/or heparin as a result of the manufacturing process. Allergic reactions to mouse protein and/or heparin cannot be ruled out. If symptoms of hypersensitivity/allergic reaction occur, discontinue the injection/infusion. In case of anaphylactic shock, the current medical standards for treatment are to be observed.
Transmission of infectious agents: Because CEPROTIN is made from human plasma, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g. viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent, and theoretically, the Creutzfeld-Jakob disease (CJD) agent.
Bleeding episodes: Several bleeding episodes have been observed in clinical studies. Concurrent anticoagulant medication may have been responsible for these bleeding episodes. However, it cannot be completely ruled out that the administration of CEPROTIN further contributed to these bleeding events. Simultaneous administration of CEPROTIN and tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) may further increase the risk of bleeding from tPA.
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT): CEPROTIN contains trace amounts of heparin which may lead to HIT, which can be associated with a rapid decrease of the number of thombocytes. If HIT is suspected, determine the platelet count immediately and consider discontinuation of CEPROTIN.
Low sodium diet/Renal impairment: Patients on a low sodium diet or who have renal impairment should be informed that the quantity of sodium in the maximum daily dose of CEPROTIN exceeds 200 mg. Monitor patients with renal impairment closely for sodium overload.
Adverse Reactions
Common adverse reactions related to CEPROTIN observed in clinical trials were hypersensitivity or allergic reactions: lightheadedness, itching and rash.
INDICATION
CEPROTIN [Protein C Concentrate (Human)] is indicated for neonates, pediatric and adult patients with severe congenital Protein C deficiency for the prevention and treatment of venous thrombosis and purpura fulminans.
Please click for Full Prescribing Information.
References:
-
CEPROTIN [Protein C Concentrate (Human)] Prescribing information. Lexington, MA: Baxalta US Inc.
-
Manco-Johnson MJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of protein C concentrate to treat purpura fulminans and thromboembolic events in severe congenital protein C deficiency. Thromb Haemost. 2016;116:56-68.