
Early diagnosis of
Severe Congenital Protein C Deficiency
Identification of Severe Congenital Protein C Deficiency (SCPCD)
Clinical diagnosis of purpura fulminans skin lesions is critical
-
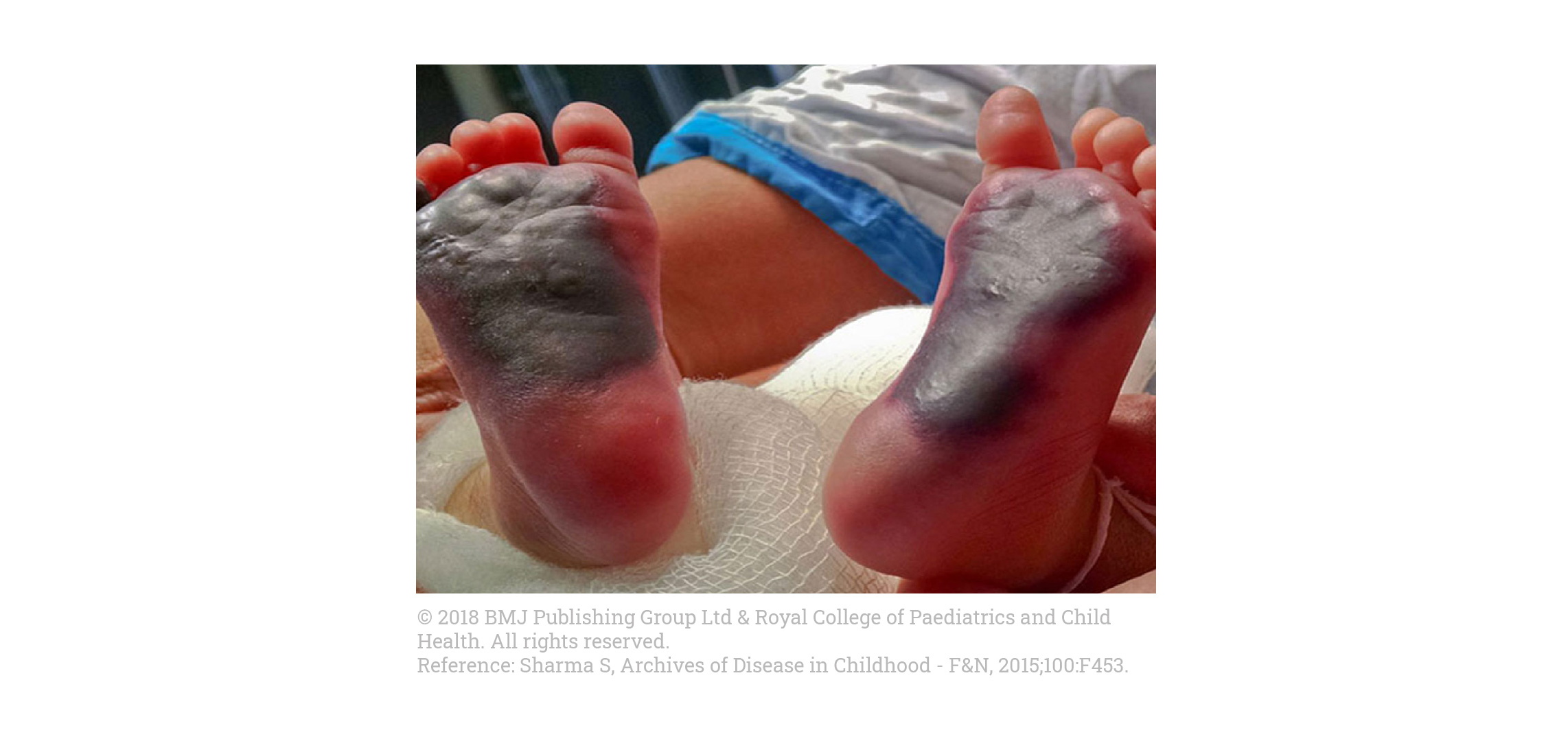
Visually identifying skin lesions:
- Infants with SCPCD usually present within hours after birth with rapidly progressive purpura fulminans1,2
- Because purpura fulminans is a hematological emergency due to the rapidly progressive nature of the multi-organ thrombotic injury, consultation with a hematologist is recommended3
SCPCD and its potential complications3
Purpura fulminans can lead to life-threatening complications:
- Purpura fulminans can rapidly progress to organ failure as a result of necrosis and disseminated intravascular coagulation3
- Rates of amputation with purpura fulminans may be as high as 62%4
Warnings and Precautions
Hypersensivity: CEPROTIN may contain trace amounts of mouse protein and/or heparin as a result of the manufacturing process. Allergic reactions to mouse protein and/or heparin cannot be ruled out. If symptoms of hypersensitivity/allergic reaction occur, discontinue the injection/infusion. In case of anaphylactic shock, the current medical standards for treatment are to be observed.
Transmission of infectious agents: Because CEPROTIN is made from human plasma, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g. viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent, and theoretically, the Creutzfeld-Jakob disease (CJD) agent.
Bleeding episodes: Several bleeding episodes have been observed in clinical studies. Concurrent anticoagulant medication may have been responsible for these bleeding episodes. However, it cannot be completely ruled out that the administration of CEPROTIN further contributed to these bleeding events. Simultaneous administration of CEPROTIN and tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) may further increase the risk of bleeding from tPA.
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT): CEPROTIN contains trace amounts of heparin which may lead to HIT, which can be associated with a rapid decrease of the number of thombocytes. If HIT is suspected, determine the platelet count immediately and consider discontinuation of CEPROTIN.
Low sodium diet/Renal impairment: Patients on a low sodium diet or who have renal impairment should be informed that the quantity of sodium in the maximum daily dose of CEPROTIN exceeds 200 mg. Monitor patients with renal impairment closely for sodium overload.
Adverse Reactions
Common adverse reactions related to CEPROTIN observed in clinical trials were hypersensitivity or allergic reactions: lightheadedness, itching and rash.
INDICATION
CEPROTIN [Protein C Concentrate (Human)] is indicated for neonates, pediatric and adult patients with severe congenital Protein C deficiency for the prevention and treatment of venous thrombosis and purpura fulminans.
Please click for Full Prescribing Information.
References:
-
Goldenberg N, Manco-Johnson M. Protein C deficiency. Haemophilia. 2008;14(6):1214-1221.
-
Price VE, et al. Diagnosis and management of neonatal purpura fulminans. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011;96(6):318-22.
-
Chalmers E, et al. Purpura fulminans: recognition, diagnosis and management. Archives of Disease in Childhood. 2011;96(11):1066-1071.
-
Gürgey A, et al. Outcome in Children With Purpura With Fulminans: Report on 16 Patients. Am J Hematol. 2005;80(1):20-5.